Guide to Writing Your MIET2510 Engineering Report
Introduction
In this guide, you will learn how to structure and format your engineering report for the MIET2510 Mechanical Design Project. This project requires you to design a vertical axis hydrogenerator’s main drive shaft, bearings, keyed joint, and shaft-to-turbine connections. Your report should effectively communicate your design process, calculations, assumptions, and CAD drawings.
Please note that this provides guidance for writing a report and is not the only way to do this, there are many ways to write a good technical report.
Structure of the Report
1. Title Page
Include:
- Project title: “Design of the Main Drive Shaft for a Vertical Axis Hydrogenerator”
- Your name and student ID
- Course title: MIET2510 Mechanical Design
- Date of submission
2. Executive Summary
Summarise the report in 150-200 words. Mention the design objective, methods used (e.g., stress analysis, material selection), and key outcomes, such as dimensions or performance metrics.
3. Introduction
Provide context for your design:
- Background: Explain the relevance of hydrogenerators and their design challenges.
- Objective: State the goal of designing key components (main drive shaft, bearings, etc.).
- Scope: Clarify the design specifications and constraints, including material selection, torque transfer, and axial/radial loads.
- Report Structure: Briefly outline the structure of your report.
4. Design Methodology
Explain your design process in detail, including:
- Component Selection: Justify material choices for the shaft, bearings, and connections, considering weight, cost, and durability.
- Calculations: Show all stress, load, and torque calculations. Detail how you determined shaft dimensions and other critical parameters.
- Bearings: Select appropriate bearings (upper guide, thrust, lower guide) and justify based on life and load conditions.
- Safety Factor: Use a safety factor of 2, as specified, and demonstrate its application in your calculations.
Where applicable, include neatly formatted equations and reference standards.
5. Results
Present your final design parameters:
- Shaft dimensions (length, diameter, material)
- Bearing selection and mounting arrangements
- Keyed and bolted connections specifications
Tables and Figures Formatting
-
Tables: Place the title above the table. Example:
Table 1: Shaft Design Results
Shaft Length (m) Material Safety Factor Max Stress (Pa) 3.5 Steel 2.0 120 MPa -
Figures: Place the caption below the figure. Example:
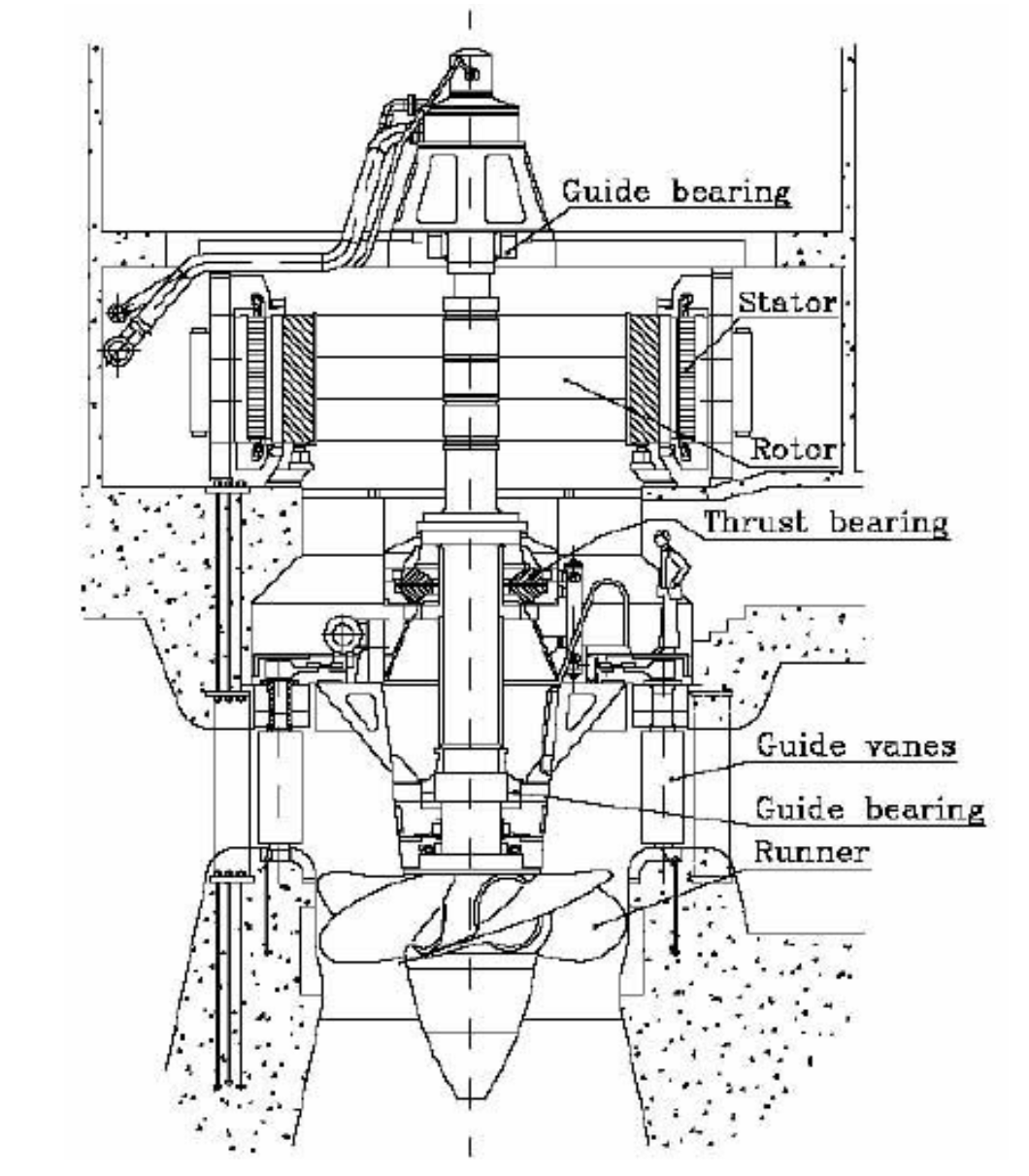 Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of Hydrogenerator
Figure 1: Schematic Diagram of Hydrogenerator
6. Discussion
Interpret your results:
- Design Implications: Discuss how your design meets the requirements (e.g., strength, reliability, efficiency).
- Comparison with Standards: Compare your design with industry standards for hydrogenerators.
- Limitations: Identify any potential limitations, such as assumptions about material properties or loading conditions.
- Recommendations: Suggest improvements for further development, such as advanced simulations or more accurate material testing.
7. Conclusion
Summarise your design process, key results, and the success of your solution in meeting the project’s objectives.
8. References
Use a consistent citation format (e.g., IEEE). Cite all textbooks, standards, and references used for calculations and material properties.
9. Appendices
Include detailed calculations, drawings, and any additional information:
- Full calculations (torque, stress, etc.)
- 2D CAD drawings of your design
Best Practices for Writing an Engineering Report
- Clarity and Precision
- Use precise engineering terminology.
- Avoid jargon unless it is well-defined within the report.
- Define key terms and explain complex concepts clearly.
- Write the report in third person (if you write in the third person, you do not talk about or acknowledge yourself or your reader in your writing. That means avoiding the words: I, me, my, you, your, we, our.)
- Logical Flow
- Organise your report in a logical, step-by-step manner, following the structure outlined above.
- Each section should flow logically from the previous one, guiding the reader through the technical information.
- Use Visual Aids Effectively
- Visual aids such as tables, figures, graphs, and diagrams can help convey complex engineering data clearly.
- Make sure every visual aid is referenced in the text and is necessary for understanding the work.
- Objectivity
- Maintain an objective tone throughout the report. Avoid personal opinions unless specifically requested in the form of recommendations.
- Consistency
- Be consistent with units, abbreviations, font sizes, and formatting throughout the document.
- Use the same citation style consistently for all references.
- Proofreading and Editing
- Carefully proofread your report to ensure that it is free from grammatical errors, typos, and formatting inconsistencies.
- Check calculations, technical terminology, and references for accuracy.