Week 1 Tutorial - Kinematics Fundamentals and Analysis of Mechanisms
Steps to Find the Mobility of a Mechanism
- Identify the Links and Joints:
- Count the total number of links ($L$) in the mechanism.
- Count the total number of 1 DOF joints ($J_1$).
- Count the total number of 2 DOF joints ($J_2$).
- Use Gruebler’s Equation:
- Substitute the values of $L$, $J_1$, and $J_2$ into Gruebler’s equation, $ M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2$ and do the calculation to find the mobility $M$.
- Interpret the Result:
- A positive value of $M$ indicates the number of degrees of freedom (mobility) the mechanism has.
- An $M$ value of 0 indicates a structure with no mobility.
- A negative $M$ value indicates an over-constrained system or a structure under pre-load.
Question 1
Draw a kinematic diagram of the following machine. Your diagram should be roughly to scale and each link should be numbered.
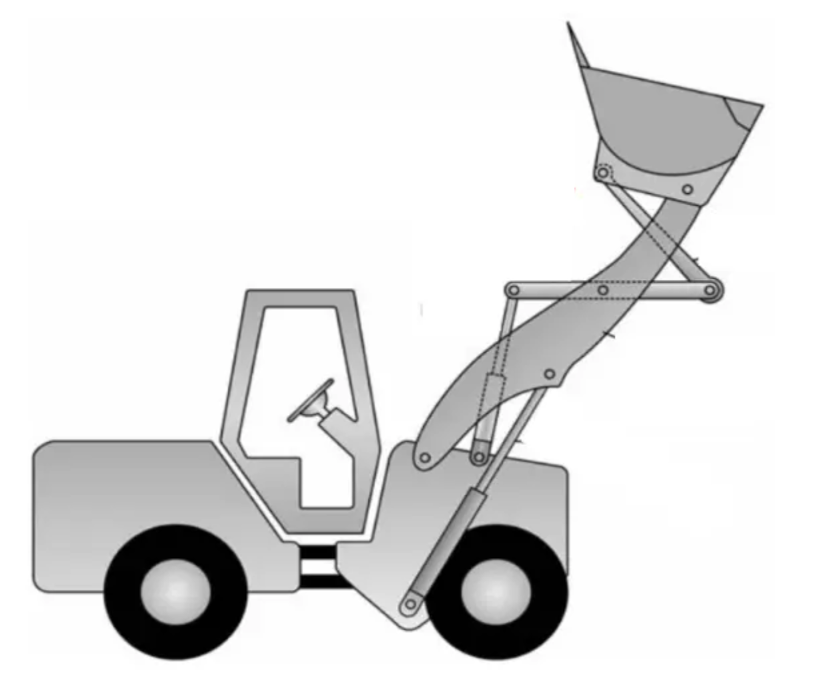
Question 2
Calculate the mobility of the linkages
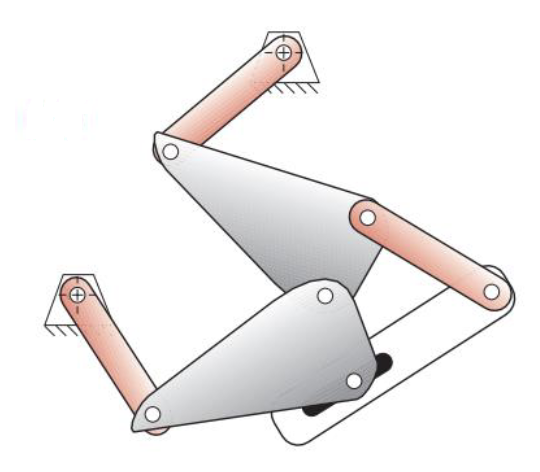
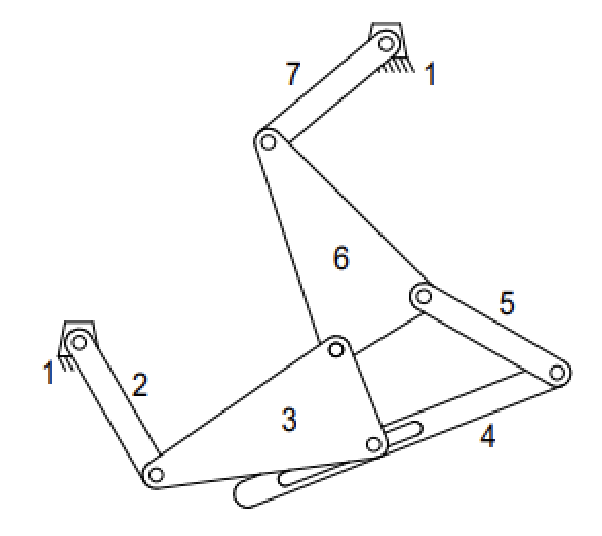
Solution
Number of links: 7
Number of 1 DOF joints: 7
Number of 2 DOF joints: 1
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[\begin{align*} M &= 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M &= 3(7-1) - 2\cdot7-1 \\ M &= 3 \nonumber \end{align*}\]Question 3
Calculate the mobility of the linkages
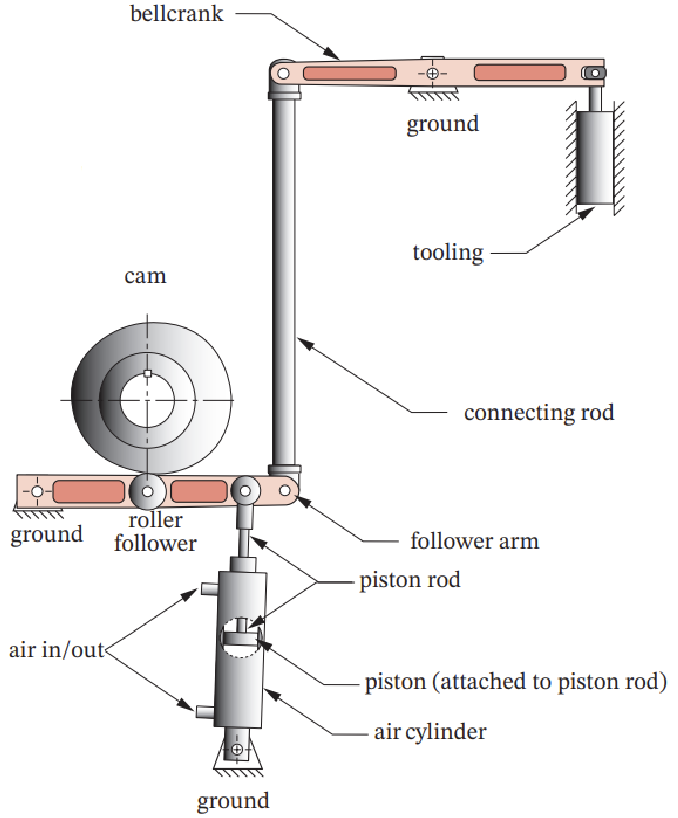
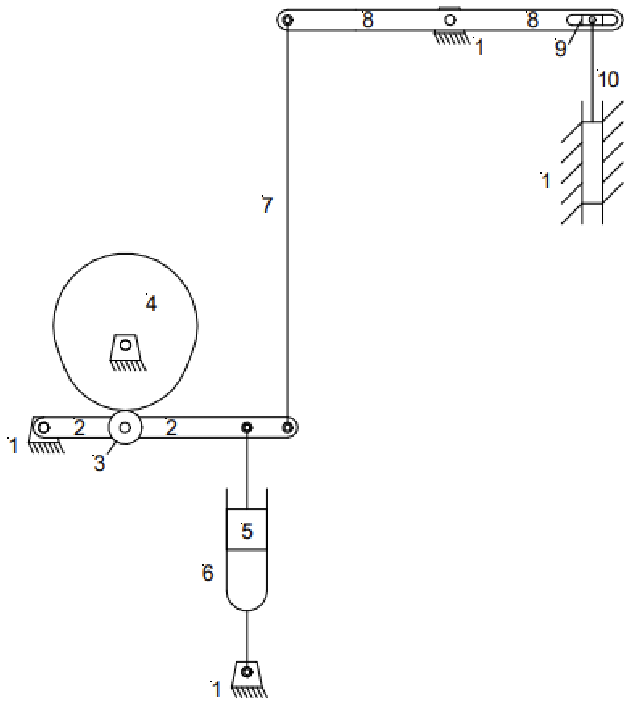
Solution
Number of links: 10
Number of 1 DOF joints: 13
Number of 2 DOF joints: 0
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[\begin{align*} M &= 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M &= 3(10-1) - 2\cdot13-0 \\ M &= 1 \nonumber \end{align*}\]Question 4
Calculate the mobility of the linkages
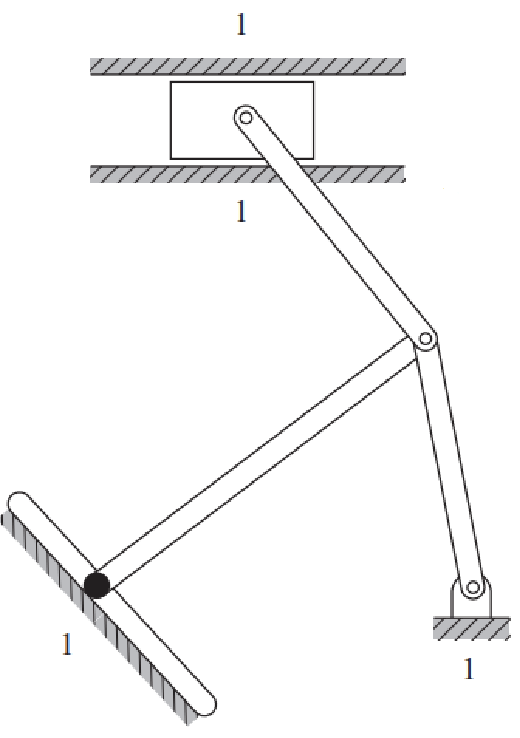
Solution
Number of links: 5
Number of 1 DOF joints: 5
Number of 2 DOF joints: 1
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M = 3(5-1) - 2\cdot5-1 \\ M = 1 \nonumber\]Question 5
Calculate the mobility of the linkages
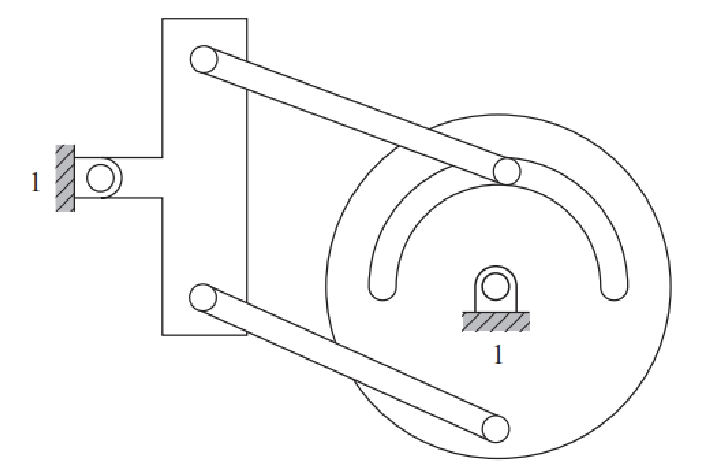
Solution
Number of links: 5
Number of 1 DOF joints: 5
Number of 2 DOF joints: 1
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M = 3(5-1) - 2\cdot5-1 \\ M = 1 \nonumber\]Question 6
Calculate the mobility of the linkages
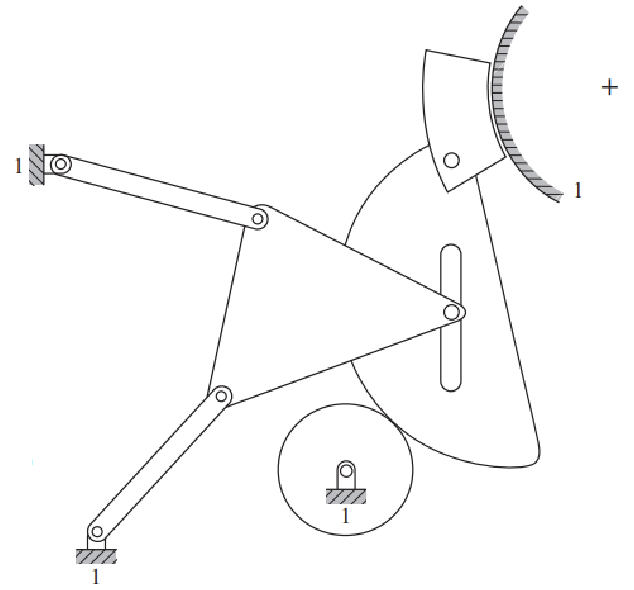
Solution
Number of links: 7
Number of 1 DOF joints: 8
Number of 2 DOF joints: 1
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M = 3(7-1) - 2\cdot8-1 \\ M = 1 \nonumber\]Question 7
Find the mobility of the ice tongs before and after grabbing
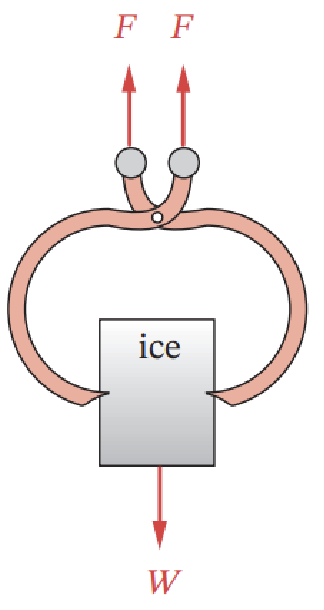
Solution
Before grabbing;
Number of links: 2
Number of 1 DOF joints: 1
Number of 2 DOF joints: 0
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M = 3(2-1) - 2\cdot1-0 \\ M = 1 \nonumber\]Number of links: 2 + 1
Number of 1 DOF joints: 1 + 2
Number of 2 DOF joints: 0
So that the mobility can be calculated.
\[M = 3(L-1) - 2J_1 - J_2 \\ M = 3(3-1) - 2\cdot3-0 \\ M = 0 \nonumber\]After grabbing, the ice tongs have 0 degrees of freedom (rigid structure), and after grabbing, tit has 1 degree of freedom.
Question 8
Find the mobility of the gas pedal mechanism
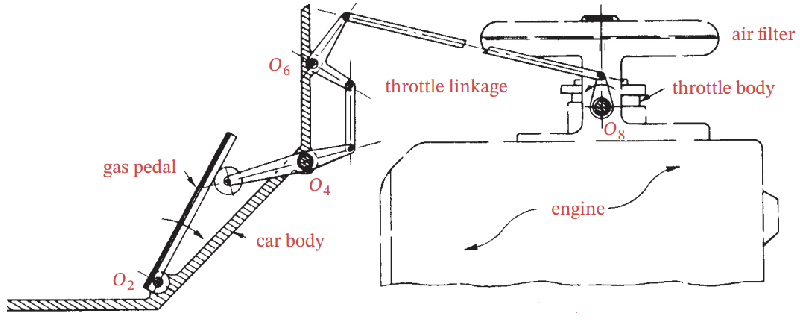
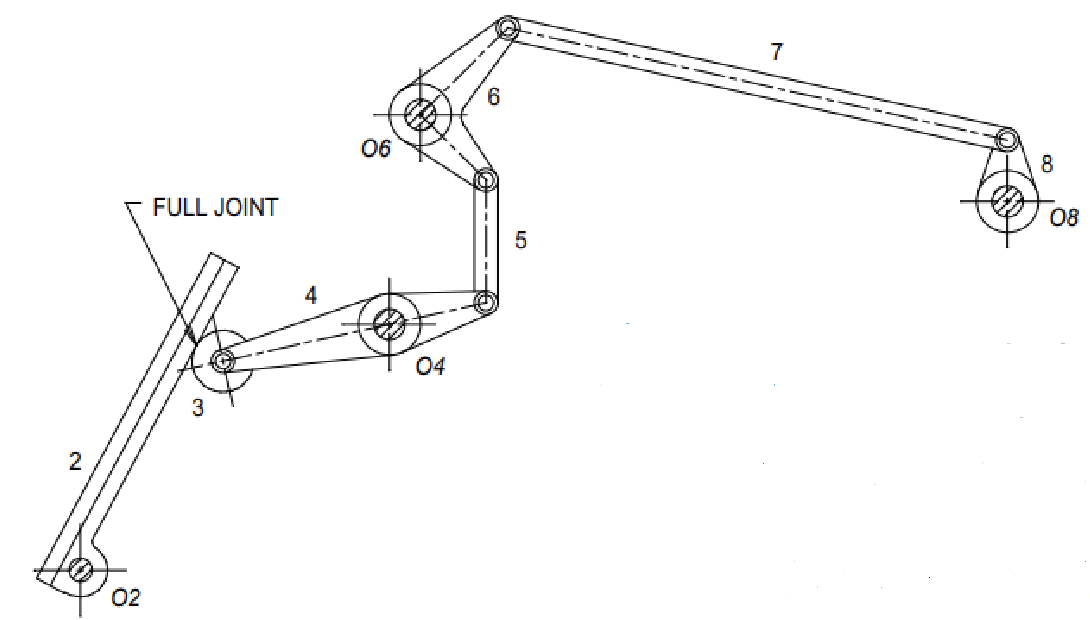
Solution
For the gas pedal mechanism:
- Number of links: 8
- Number of 1 DOF joints: 10
- Number of 2 DOF joints 0
Question 9
Using the kinematic diagram you drew in Question 1 calculate the mobility of the mechanism using Gruebler’s equation.